Post written by Wade W., BI Consultant at Ideaca. Read more about BI on his blog: Pragmatic Business Intelligence.
If your company is a well-known brand, somebody, somewhere is publicly talking about it. Right now. It may be on your own Social channels, in an Internet forum, a blog or other user-generated content site. Social Media Monitoring, which put simply is keeping a constant eye on Social sites including Twitter, Facebook and hundreds of other platforms to monitor what is being said about your brand, has become a necessity for most large organizations, and it is an art and a science to manage this well. Manage it badly, and you can have a catastrophic image issue (i.e. the 2010 Nestle Palm Oil debacle on Nestle’s own Facebook page). Handle it well, and you can cement a solid relationship with existing clients and convert new clients to your brand (i.e. HP’s little-known but truly brilliant efforts to provide temporary replacement HP hardware to certain individual users on social platforms complaining of broken computers).
From a commercial aspect, companies are increasingly looking at Social Media to contribute to driving revenue, largely through lofty concepts such as “engagement” and “conversion.” Social is unique in not only the speed of the communication, but also the intimate nature of content. In addition, and importantly, what companies must understand is that in the Social realm, the customer controls the conversation. The implication here is a fundamental paradigm shift for Customer Relationship Management and Marketing, to understand the customer on a personal level, and to handle – with great sensitivity – both the positive and negative sentiment expressed on Social platforms.
(Social) Business Intelligence
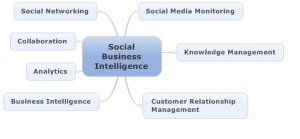
A growing and compelling new flavor of Business Intelligence is attempting to tap into the unstructured content on social platforms and attempt to structure that data into a format that can be analyzed and mined using new methods such as Sentiment Analysis, which measures the aggregate sentiment across user posted content. Social Business Intelligence uniquely sits in the convergence of Knowledge Management, Social Media Monitoring, Collaboration, Social Networking, Analytics , Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and Business Intelligence (BI).
First, there is an important roadblock to get out of the way. Today there are a selection of tools to do everything I am discussing below in one way or another. With a simple sentence I have rendered technology irrelevant for the purposes of this blog. So let’s focus on what Social BI is, how it is done and what it means because that is what is important to business.
I’m not really a catch-word kind of guy, but this is Big Data in its truest form. There are thousands of platforms and sites, of course, but if we only talk about the current Big Guys (Facebook, Twitter and Foursquare for example), this would add up to billions or trillions of conversation segments over a given (even conservative) time horizon. To put this in context: that customer data warehouse you have built over all these years probably doesn’t come close…
Social Business Intelligence offers both Internal and External Opportunity
There are both internal and external opportunities to be realized through Social Media Business Intelligence, and many tools are evolving to support these, some even going so far as to adopt a “Facebook-like” or “Twitter-like” interface, mimicking social interaction and Social Networking site features.
Social Business Intelligence applied internally to an organization could be termed Social Collaboration. For example, certain tools might feature collaborative review where colleagues can ask questions and link those answers to specific reports, or collaboratively comment and markup objects such as Business Intelligence ad-hoc analytics, graphs or reports. This functionality to comment in real time on powerful business intelligence (even if it is only based on Traditional data sources that exclude Social Media data) has the potential to add value to interpretation of the reports that companies produce and use today to base key decisions upon, thereby potentially improving decisions made from today’s Decision Support Systems. Many traditional software vendors already have adopted such functionality.
Of course, where Social Business Intelligence as a disruptive technology becomes particularly interesting is when we start gathering and analyzing that unstructured user-generated content, or even more compelling, when we combine it with our existing “traditional” Enterprise Analytics environments. This empowers organizations to produce new innovative products that target user segments more accurately and respond better to customer support or relationship development opportunities. The value of Social Business Intelligence is not really “about” the frequency of words and phrases users post on social platforms. The value is in segmenting, categorizing, mining and understanding the aggregate of the users’ behavior, and the sentiment of those posts across products, segments and channels.
Social Media has its own unique segments, which include Employees, Partners, Influencers, Detractors and Advocates. We can analyze social network traffic, understand and identify our segments, and tailor personalized/semi-personalized interaction to individuals or one of these segments, flagging key comments, monitoring Likes, +1’s, trending subjects and use of hashtags, enabling rapid and targeted response to user comments to avert public relations crisis, measure success of our Social Marketing programs or capitalize on new opportunities.
It’s all about the conversation. And you don’t control it.
Again, companies need to understand that the customer controls the conversation. However, the tools exist that can arrange and present structured knowledge from unstructured noise, providing key information input to areas such as Marketing and Manufacturing to be responsive and agile, acting on data that correlates highly to real-life fact.
At its root, Social Media is about the conversation. This implies new requirements for how to manage our link to the customer, and how to most effectively target and market to them. Increasingly, consumers are mistrustful of the marketing messages and advertising. They are more likely to find more relevance and see more value in the reviews and purchasing of their friends and peers.
Social Business Intelligence in Practice
I thought to finish, I would provide two examples that support the claim that through mining user-generated content, we can correlate with very high level of confidence, to known and validated facts.
Google Flu Trends
An example of single-source user generated content analysis is Google Flu Trends. Google has been analyzing aggregated web search terms to see if it is possible to correlate geographic frequency of user search terms on Google’s search engine to real data on flu epidemics.
While I recognize this is not Social Media per se, this example is very relevant to the argument that user-generated content can be tied to sentiment and can also be used as a predictor for future events, when we clearly understand and define the objective, then identify and measure indicators supporting that objective.
Google’s site http://www.google.org/flutrends/ca/#CA provides up-to-current-day results to allow tracking of current and developing flu incidents and epidemics. In addition, on this site there are historical graphs over a multi-year period for regions around the globe that prove, using known, validated historical data, that reality and future events can indisputably be predicted by user-generated content.
United Nations Global Pulse.
Between 2009 and 2011, the United Nations and SAS studied how Social Media and other user-generated content from public internet sources such as blogs, Internet forums, and news published in Ireland and the US could be correlated to validated statistics and leveraged as a compliment and an qualitative indicator of real-life events.
For Global Pulse, the focus was on employment status. To summarize from the document found at http://www.sas.com/resources/asset/un-global-pulse.pdf, the UN identified keywords indicating changes in employment status (i.e.”fired”), level of anxiety (i.e. “depressed”) or economic indicators (i.e. loss of housing or auto repossession, cancellation of vacations) in order to monitor sentiment. The results were astonishing. The analysis of sentiment allowed them to predict increases in unemployment as much as four months in advance of an uptick in unemployment claims with a 90-95% level of confidence. Further, they were able to predict precisely, again with a 90-95% confidence, how long after an uptick in unemployment that there would be an increase in clear economic indicators in the form of talk of loss of, or negative changes to housing, changes of transport method or cancellation of travel plans.
These two examples underscore that user-generated content in the social realm represents a new and potentially highly accurate source of knowledge when tied to clearly defined objectives and supporting metrics (leveraging appropriate keywords). Indeed, Social Media Business Intelligence has the potential to facilitate very personal customer understanding and when backed by a well defined strategy, to strengthen the relationship with our customer, avert PR disasters and increase customer engagement and conversion.
What are your thoughts? Is the world ready for Social Business Intelligence? Has your company thought about imposing order and structure to the chaos that is Social Media user-generated Content?

0 comments:
Post a Comment